Chondral Defects - Diagnosis
How is articular cartilage damage diagnosed?
It can be difficult to diagnose an articular cartilage injury. Physical examination may show a swollen knee, but frequently the exam is normal.
Imaging may help the doctor make a diagnosis in some, but not all, cases. X-rays may be normal in most cases because only bone damage is visible on X-ray. One indication of advanced cartilage loss is a decrease in space between two bone surfaces. A loose bone fragment may be detected in a condition called osteochondritis dissecans (OCD), in which a portion of bone detaches with the articular cartilage.
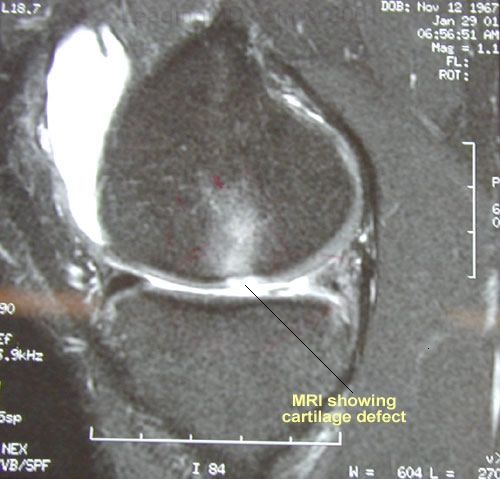
An MRI (Magnetic Resonance Image) may reveal softened cartilage in many cases. This softening can be difficult to detect, however, and the diagnosis may require the most sensitive and highest quality MRI images, which may show changes in the underlying bone. Cartilage thinning or loss is also usually visible on MRI.
Articular cartilage damage is most reliably diagnosed with an arthroscopic examination of the joint. In this procedure, a tiny fiberoptic scope is inserted into the joint. The doctor uses this scope to visually assess the damage.
BackNext